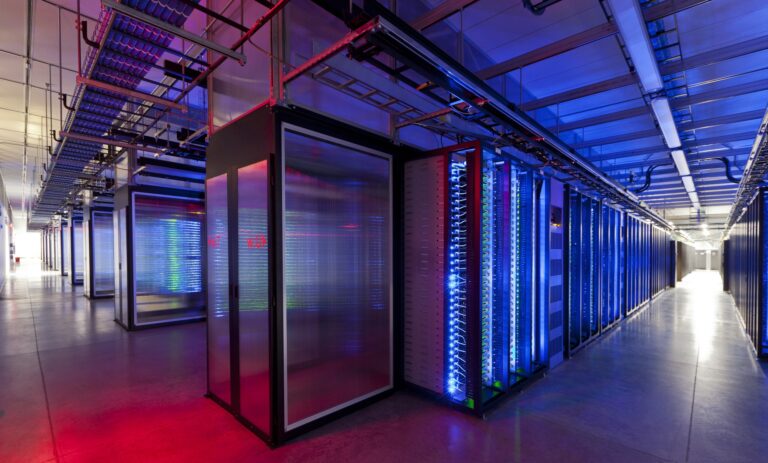
As we look ahead to the future, cloud computing will continue to evolve and shape the way businesses and individuals interact with technology. With its flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, the cloud offers a transformative solution to meet the diverse needs of modern enterprises. Whether you are a small business or a large enterprise, understanding the fundamental concepts of cloud computing is essential for making informed decisions about how to use these technologies effectively.
By Randy Ferguson
What Are the Main Cloud Computing Models?
Cloud computing models provide different layers of services to meet various business and individual needs. The three main models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). These models are essential building blocks for the cloud computing ecosystem, each serving different purposes and target audiences.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides businesses with the most flexibility in terms of computing resources. It offers virtualized hardware over the internet, including servers, storage, and networking. This model is ideal for businesses that need to manage their own infrastructure but without the upfront investment in physical hardware. Companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure offer these types of services, enabling companies to scale quickly and only pay for what they use.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS is designed for developers. It provides a framework that allows them to develop, test, and deploy applications without worrying about the underlying hardware or software layers. In this model, cloud service providers offer tools, services, and programming languages to help developers create applications more efficiently. Examples of PaaS include Google App Engine and Heroku, which provide cloud environments for building scalable apps.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS is a model where cloud service providers host software applications and make them available over the internet. With SaaS, users do not have to worry about installation, maintenance, or hardware management. Instead, they simply access the software via a web browser. Popular SaaS applications include Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), Microsoft 365, and Salesforce, which are widely used by businesses and individuals alike.
Deploying Public, Private, or Hybrid Clouds
Understanding cloud computing models is crucial for enhancing Europe’s digital sovereignty. By effectively leveraging these models, European nations can ensure data security and control, ultimately fostering trust among citizens. This strategic approach is integral to europe’s path to digital sovereignty and fairness, enabling a more balanced digital landscape across the continent.
Cloud computing has transformed the way businesses and individuals interact with technology. Since CloudTweaks was founded over 15 years ago, we have been at the forefront of covering the cloud technology revolution. Over the years, we have seen cloud services evolve from a niche offering to an essential component of modern IT infrastructure. In this article, we’ll guide you through the fundamental cloud computing for beginners models and concepts so that you can understand how these services can benefit your business or personal needs.
- Public Cloud: A public cloud is a cloud infrastructure that is shared by multiple organizations and is owned by a third-party cloud provider. The most common example of a public cloud is Amazon Web Services (AWS). These services are available over the internet, and customers can access them on-demand, paying only for the services they use. Public clouds offer great scalability and flexibility, making them an excellent choice for businesses with variable or unpredictable workloads.
- Private Cloud: A private cloud is used exclusively by one organization. It is hosted either on-premises or by a third-party provider, but the infrastructure is dedicated to that particular organization. Private clouds provide greater control over data and security, making them ideal for businesses with specific compliance or regulatory requirements. These clouds are often used by industries such as healthcare and finance.
- Hybrid Cloud: A hybrid cloud combines elements of both public and private clouds. It allows businesses to keep critical workloads on a private cloud while taking advantage of the public cloud for less sensitive applications. This model provides more flexibility and the ability to scale based on needs. Hybrid clouds are particularly useful for businesses that need to maintain a high level of security but also want to capitalize on the cost savings of public cloud services.
Cloud Computing Characteristics to Know
While cloud computing offers many benefits, there are also some challenges that businesses need to consider. Addressing these issues is crucial for businesses to make the most of their cloud investments.
- Elasticity and Scalability: One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is its ability to scale resources up or down based on demand. Elasticity refers to the cloud’s ability to automatically adjust resources to match the current needs of users, whether they need more power during a peak period or less during off-peak times. This scalability is what allows businesses to grow without the need for large capital expenditures on physical infrastructure.
- Self-Service Provisioning: Cloud services enable users to request resources such as storage, processing power, and software applications without needing intervention from the cloud service provider. This self-service model makes cloud computing fast and efficient, allowing businesses to quickly adapt to changing conditions.
- Standardized Interfaces: Cloud services use standardized interfaces, such as APIs, to ensure that different systems and applications can communicate effectively. This interoperability makes it easier for businesses to integrate various cloud services into their existing IT infrastructure, creating a seamless experience for users and developers alike.
- Billing and Usage Metering: The pay-as-you-go model is one of the primary reasons businesses embrace cloud computing. With cloud services, businesses only pay for the resources they actually use, instead of committing to large upfront investments in hardware. This model ensures that companies can scale their usage up or down depending on their current needs, making cloud computing more cost-effective than traditional infrastructure.
Common Issues in Cloud Computing
When it comes to deploying cloud services, businesses can choose from three primary types of cloud environments: public, private, and hybrid clouds. Each option has its own set of advantages and challenges, depending on the specific needs of the organization.
- Security: Security is a major concern when it comes to cloud computing, as businesses must trust third-party providers with their data. Implementing strong encryption, identity management, and access control measures is essential to protecting sensitive information. In addition, businesses must ensure that their cloud provider complies with relevant security standards and regulations.
- Manageability: Managing cloud-based services across multiple platforms can be complex. Ensuring that the cloud infrastructure is well-managed, with proper monitoring and performance metrics in place, is essential to maintaining service quality and efficiency.
- Compliance: Compliance with industry regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, is a critical consideration when using cloud services. Businesses must ensure that their cloud provider offers the necessary tools and services to meet regulatory requirements, especially when dealing with sensitive data such as personal health information or financial records.
- Data Privacy and Portability: With data moving across different cloud environments, businesses need to ensure that their data remains private and secure. They also need to consider the portability of their data, ensuring that it can be easily transferred between different cloud providers if necessary. This is particularly important for businesses that may want to switch providers or operate in a multi-cloud environment.
How Does Understanding Cloud Computing Models Contribute to Europe’s Digital Sovereignty?
(Updated from: 06/22/2010)
Final Thoughts: Cloud Computing for the Future
Understanding the core characteristics of cloud computing is essential to leveraging its full potential. Here are some of the key attributes of cloud services that make them so appealing to businesses and individuals alike.