Jul 29, 2025
Ariffud M.
In n8n, looping over items is one of the most powerful techniques for handling lists of data, such as email addresses, API responses, or database records.
While many n8n nodes process items individually by default, some situations require more control – for example, when you need to send messages in batches or limit the number of requests per cycle.
That’s where the Loop Over Items (Split in Batches) node comes in. You define a batch size, and it splits the dataset into smaller groups, processing each batch one at a time.
This article explains what looping means in n8n, how the Loop Over Items node works, and when to use it. You’ll also learn how to iterate over items through practical examples, such as sending bulk emails and processing large datasets in manageable chunks.
What does looping mean in n8n?
In n8n, looping refers to repeating a set of actions for each item in a list or array within a workflow. This lets you automate tasks for every item in a dataset without manual intervention.
For example, if you have a list of 100 contacts and want to send an email to each one, looping lets n8n process each contact sequentially (sending one email after another) rather than sending bulk emails to all of them at once.
By default, many n8n nodes process incoming arrays or lists item by item. When a node receives an array, it passes each item down the workflow, one at a time.
But explicit looping becomes necessary when a node can only handle a single item at a time, when you need more control over the order and batching of operations, or when handling too many items at once could overwhelm your system.
How does the Loop Over Items node work in n8n?
The n8n Loop Over Items (Split in Batches) node works by dividing an incoming list of items into smaller, manageable batches and processing them one batch at a time.
By defining a batch size, you can control how many items flow through your workflow in each iteration.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of how it works:
- The Loop Over Items (Split in Batches) node splits an array of input items into batches based on the size you define, such as one item per batch.
- Each batch is then passed to the next connected node, which performs the desired action, such as sending an email or making an API request.
- After processing a batch, the workflow returns to the Loop Over Items node to continue processing the next set of items.
- This repeats automatically until all batches are processed.
The Loop Over Items node processes only the list of items it receives and then stops, so you don’t need to worry about it looping forever.
But if you use it to handle paginated data, such as fetching pages from an API, you must add conditional logic – like an If node – to check if there are more pages.
This condition tells the workflow when to stop, preventing it from looping through empty pages.
When should you use the Loop Over Items node?
You should use the Loop Over Items node when you need to split data into smaller chunks and process items one by one.
This is especially useful for large datasets, when each item requires individual action, or when you want to control the number of items processed in each iteration.
Examples of when to use the Loop Over Items node include:
- Sending individual emails or messages to each contact in a list.
- Making separate API calls for each entry in a dataset, such as updating customer records.
- Processing records from a spreadsheet or database one by one, ensuring each row is handled individually.
- Handling paginated API responses to fetch all available data from an API through multiple requests.
- Generating and sending personalized reports or invoices for each client in a list.
- Monitoring the status of multiple servers or websites by checking each one individually and logging the results.
Expert tip
The Loop Over Items (Split in Batches) node is commonly used for a fixed number of batches, similar to a for loop in the programming world. It’s used when you want to perform a specific action a set number of times before continuing to the next step.
How do you loop over items in n8n?
To loop over items in n8n, combine several nodes to process each item individually in a list.
Loop Over Items (Split in Batches) is the main node for this, but you’ll pair it with other nodes, such as Edit Fields (Set) to prepare data, HTTP Request to interact with external services, and If to add logic or define stopping conditions.
A general structure for looping over items looks like this:
- Input – start with a node that provides a data source, such as Edit Fields (Set) or Google Sheets.
- Split Out (optional) – add this node if your input node can’t split data into individual items.
- Loop – use the Loop Over Items (Split in Batches) node to divide the list into smaller batches, typically one item per batch (or more, depending on your needs).
- Process – add a processing node, such as HTTP Request, if you need to interact with external services, or other third-party tool nodes, depending on your workflow.
- If or Wait (optional) – use the If node to apply conditions or manage pagination, and add Wait to pause after one iteration before continuing.
- End – the loop completes automatically once all items are processed.
Next, let’s explore three practical use case examples to see how this setup works in real-world scenarios.
Sending bulk emails in controlled batches
In this example scenario, you have 100 email addresses and want to send messages in batches of five at a time, with a five-minute pause between batches.
Why is looping needed?
Email service providers apply strict rate limits on outgoing emails. Sending 100 emails at once can exceed these limits, resulting in failures or temporary account suspensions.
Looping with delays between batches helps you stay within these limits, maintain a legitimate sending reputation, and reduce the risk of your emails being marked as spam.
Instructions to send bulk emails in controlled batches in n8n:
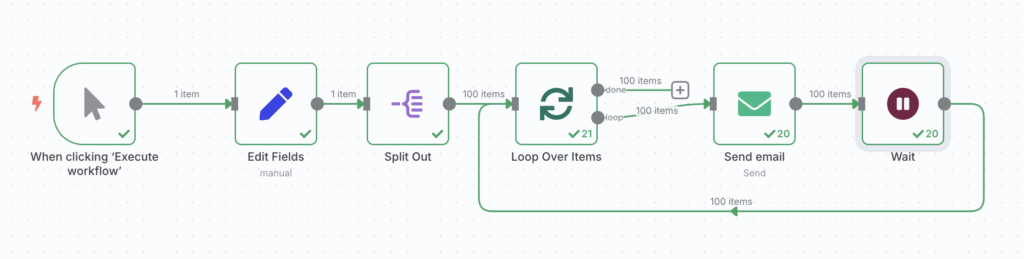
- Start with Manual Trigger
Drag the Manual Trigger node to the canvas to start the workflow.
- Prepare the email list
Use the Edit Fields (Set) node to create an array of 100 dummy email addresses. Set the following:
- Name: emails
- Type: array
- Value: ={{ Array.from({length: 100}, (_, i) => email${i + 1}@example.com) }}
If you’ve already connected n8n to Google Sheets, you can pull real email addresses from a spreadsheet using the Google Sheets node instead.
- Split the array into individual items
Add a Split Out node and set the field to emails to separate the array into individual email items.
- Group items into batches
Add the Loop Over Items (Split in Batches) node and set the batch size to 5. This will process the emails in groups of five.
- Send the emails
Use the Send Email node to configure the following settings:
- From Email: your sender email address
- To Email: ={{ $json.emails }}
- Subject: “Test email”
- Email Format: text
- Text: “Hey, this is a test email via n8n.”
Also, set up SMTP credentials for your email provider.
- Pause between batches
Add a Wait node and set the unit to minutes with a value of 5, creating a five-minute pause after each batch.
- Loop until all emails are sent
Connect the Wait node back to Split in Batches to continue looping until all emails are processed.
Handling large datasets with batch processing
Imagine if you needed to process a large dataset while respecting rate limits or system constraints. This workflow processes 500 customer records in batches of 10.
Why is looping needed?
Many APIs impose rate limits, such as 100 requests per minute. Processing all 500 records at once exceeds these limits, causing failures.
Looping divides the data into smaller chunks, preventing overloads on n8n and the target system while ensuring smoother, more reliable processing.
Instructions to handle large datasets with batch processing in n8n:
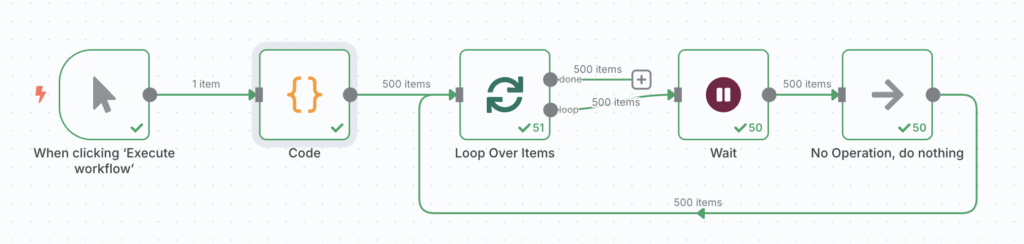
- Set up the workflow trigger
Use the Manual Trigger node to initiate the process.
- Generate customer records
Use the Code node to create 500 dummy customer records using the JavaScript code below:
const customers = [];
for (let i = 1; i <= 500; i++) {
customers.push({
id: i,
name: `Customer ${i}`,
email: `customer_${i}@example.com`,
registration_date: new Date().toISOString().slice(0, 10)
});
}
return customers.map(customer => ({json: customer}));
If available, you can use real customer data using the Google Sheets or PostgreSQL node.
- Split the data into batches
Add the Split in Batches node, set the batch size to 10, and disable the Reset option.
- Pause between batches
Insert the Wait node after Split in Batches to introduce a delay between batches. Set the interval to 90 seconds, or as you prefer.
- Set up processing actions
Add the No Operation, do nothing node as a placeholder. Later, replace it with an HTTP Request node to send each batch of customers to the target API, such as a CRM or email service.
- Create the loop
Connect the No Operation, do nothing node back to Split in Batches, so that the loop continues until all batches are processed.
This scenario assumes you want to set up an automated system that fetches content from multiple RSS sources – Hostinger Tutorials and Blog – sequentially, with controlled delays.
Why is looping needed?
Making simultaneous requests to multiple RSS feeds, whether from the same or different domains, can be mistaken as aggressive behavior.
Looping with delays helps manage server resources, reduces the risk of IP blocking or rate limiting, and ensures reliable access to the feeds.
Instructions to process multiple RSS feeds sequentially in n8n:
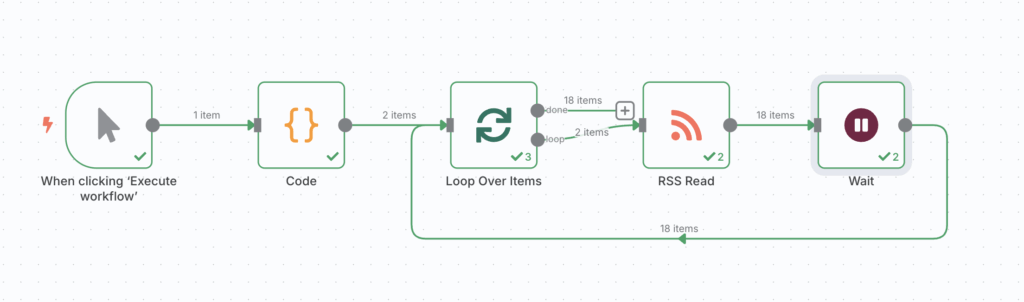
- Trigger the workflow
Start the workflow by using the Manual Trigger node.
- Define RSS feed URLs
Add the Code node to define the feed URLs with this JavaScript code:
return [
{ json: { url: 'https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/feed' } },
{ json: { url: 'https://www.hostinger.com/blog/feed' } }
];
Modify or add more URLs as needed.
- Split feeds into individual items
In the Split in Batches node, set the batch size to 1 to process one feed at a time.
- Read RSS feeds
- Connect the RSS Read node after Split in Batches.
- Set the URL parameter to ={{ $json.url }} to use the dynamic feed URL from each batch.
- Add a delay between requests
Set a 15-minute delay in the Wait node to prevent sending requests too quickly.
- Create the loop
Connect the Wait node back to the Split in Batches node to continue processing all feeds.
What are the best tips when looping over items in n8n?
Several best practices when looping over items in n8n to avoid issues and keep your workflows clean are listed below:
- Use the Split Out node when your input is a single JSON array that hasn’t been divided into individual items.
- Set the Loop Over Items (Split in Batches) node to a batch size of 1 for item-by-item processing, or increase it if bulk handling works for your case.
- Always connect the loop back from your processing node to Loop Over Items (Split in Batches) to continue until all items are handled.
- Define a clear exit condition to prevent infinite loops, especially when working with pagination or repeat-until logic.
- Avoid unnecessary loops, as many n8n nodes already support array inputs and process each item automatically.
- Respect API rate limits by adding a Wait node between requests to avoid throttling or blocks.
- Keep your loop lean. The fewer nodes inside it, the better the performance and maintainability.
Where should you host your n8n workflows?
If you’re building n8n workflows that loop over items, schedule tasks, or run in production, you need a stable, always-on environment.
Running n8n locally works for testing, but it comes with major drawbacks: your computer must stay on, and scheduled tasks will fail if the device sleeps or loses internet access.
For reliable performance and uptime, we suggest hosting n8n on a virtual private server (VPS). A VPS keeps your workflows running 24/7, enables secure remote access, and scales with your automation needs.
With the n8n VPS solution from Hostinger – starting from $4.99/month – n8n and all required components come preinstalled, so you don’t need to install everything manually.
You can run advanced automations without interruption, supported by powerful hardware and infrastructure that guarantees 99.9% uptime.
Scaling is simple. With up to 8 vCPU cores, 32 GB of RAM, 400 GB of NVMe storage, and 32 TB of bandwidth, you can start small and upgrade with just a few clicks as your workflows grow.
What’s next to learn after looping over items in n8n?
Now that we’ve covered how to loop over items in n8n, you can start using one of the most powerful patterns for building dynamic, flexible workflows.
Whether you’re sending personalized emails, processing paginated API data, or syncing entries across tools, looping gives you full control to automate tasks batch by batch.
From here, try advanced actions to scale, optimize, and combine looping with other logic, such as:
- Merge processed results using the Merge node.
- Trigger follow-up workflows or API calls based on loop output.
- Store or analyze data in databases, spreadsheets, or dashboards.
- Send summary notifications through email, Slack, or other channels.
- Clean up temporary data or log entries for future tracking.
Also, to build smarter automations, explore more n8n workflow examples to see how looping fits into larger, more advanced setups.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to
Hostinger’s rigorous editorial standards and values.