Aug 11, 2025
Jordana A.

As organizations race to deliver software faster and more securely, new tools and practices are reshaping how code is written, tested, and deployed. AI is transforming how teams approach development and security, while interest in low-code platforms, progressive web apps, and cloud-first strategies reflects evolving business needs.
Whether you’re an emerging developer or a business owner looking to stay ahead, understanding the latest software development trends can help you plan for what’s next. From AI to DevSecOps and cloud computing, see how these changes are shaping the future of software and the teams behind it.
Top 10 software development trends in 2025
Here are the key trends in software development influencing the industry:
- Nearly half of AI projects focus on IT automation.
- By 2026, AI will automate half of network operations in 30% of enterprises.
- 4 in 5 companies consider low-code approaches strategically important.
- Low-code technologies will power 75% of new apps by 2026.
- Asia Pacific leads progressive web app (PWA) market growth with the fastest CAGR of 32.7%.
- Asia Pacific is experiencing the fastest growth in the progressive web app (PWA) market globally.
- 9 in 10 companies use a multicloud strategy and report improved security after making the switch.
- 76% of organizations are implementing Zero Trust, but only 35% have fully deployed it.
- Automation trends will create 97 million new jobs in managing and operating automated systems.
- 75% of AI developers spend only 21% of their time writing new code.
How AI is transforming software development
From code suggestions to automated testing, the latest technologies in the software industry are streamlining workflows and improving efficiency throughout the development lifecycle. These trends show how AI-driven software development is setting the standard for modern practices.
- The generative AI market is expected to reach $1.3 trillion by 2032. AI statistics show that over 95% of executives believe it will fundamentally change how AI is applied in business and development, highlighting its rapid expansion across industries (Hostinger).
- $15.7 billion in market value by 2033. The global market for AI in software development is projected to grow from $1.37 billion in 2026, with a strong CAGR of 42.3%. North America leads this growth, holding a 42.1% revenue share in 2024 (Grand View Research).
- 47% of AI deployments target IT automation. AI trends in business highlight that IT and engineering teams are leading this shift, with 62% already at moderate or advanced stages of AI adoption (Hostinger).
- By 2026, 30% of enterprises will use AI to automate half their network operations. LLM statistics show a sharp rise from less than 10% in 2023, reflecting a broader shift to hyperautomation (Hostinger).
- Nearly 8 in 10 companies have deployed generative AI. Yet most see little impact on profits, creating the “gen AI paradox.” This gap comes from overusing chatbots while better, more specific tools are still being tested. AI agents may offer a way forward by enabling smarter, goal-driven automation (McKinsey).
- Agentic AI will resolve 80% of customer service issues by 2029. This shift is expected to cut operational costs by 30%. Unlike traditional GenAI tools, agentic AI takes action on behalf of users, advancing automation and customer support (Gartner).
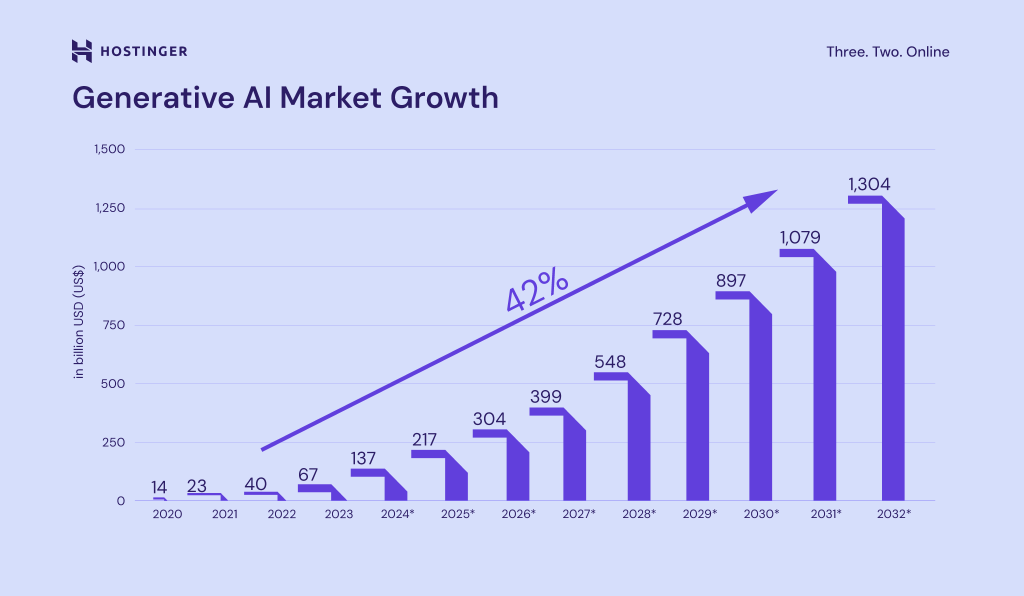
With a strong 42.3% CAGR, this surge of AI adoption reflects growing demand for smarter automation, faster release cycles, and more adaptive development workflows. It’s safe to say this technology is not just a trend ‒ it’s shaping the future of how software is developed, maintained, and scaled.
Trends in low-code and no-code development
Low-code and no-code platforms are gaining traction as businesses look for faster, more cost-effective ways to build applications. These software development tools simplify the process by minimizing manual coding, helping teams prototype and deploy faster. The following trends highlight just how rapidly low-code adoption is growing across the industry.
- $101.7 billion in market value by 2030. Low-code trends project that the global low-code market will grow from $45 billion in 2026, with a strong CAGR of 22.3%. North America leads adoption, driven by demand for faster development and digital transformation (Hostinger).
- 4 in 5 companies see low-code as strategically important. Businesses value low-code for its speed and impact: 80% say it accelerates app development, while 79% believe it improves IT operations and supports transformation projects (Hostinger).
- Three-quarters of new app development will use low-code tools by 2026. Rising demand for automation and a shortage of skilled developers make the low-code approach a key solution for modern software teams (Hostinger).
- 80% of low-code and no-code users will be outside IT by 2026. Up from 60% in 2021, this shift shows how companies are empowering non-developers to build apps faster and create custom workflows with low-code tools (Hostinger).
- Up to 90% faster app development with low-code platforms. Companies also report up to 70% cost savings compared to traditional development, often breaking even within just 6 to 12 months (Hostinger).
- 84% of enterprises say low-code platforms ease IT strain. These tools speed up delivery, ease the load on IT teams, and involve business stakeholders in app creation. As a result, 91% of users experience better IT agility and innovation. (Hostinger).
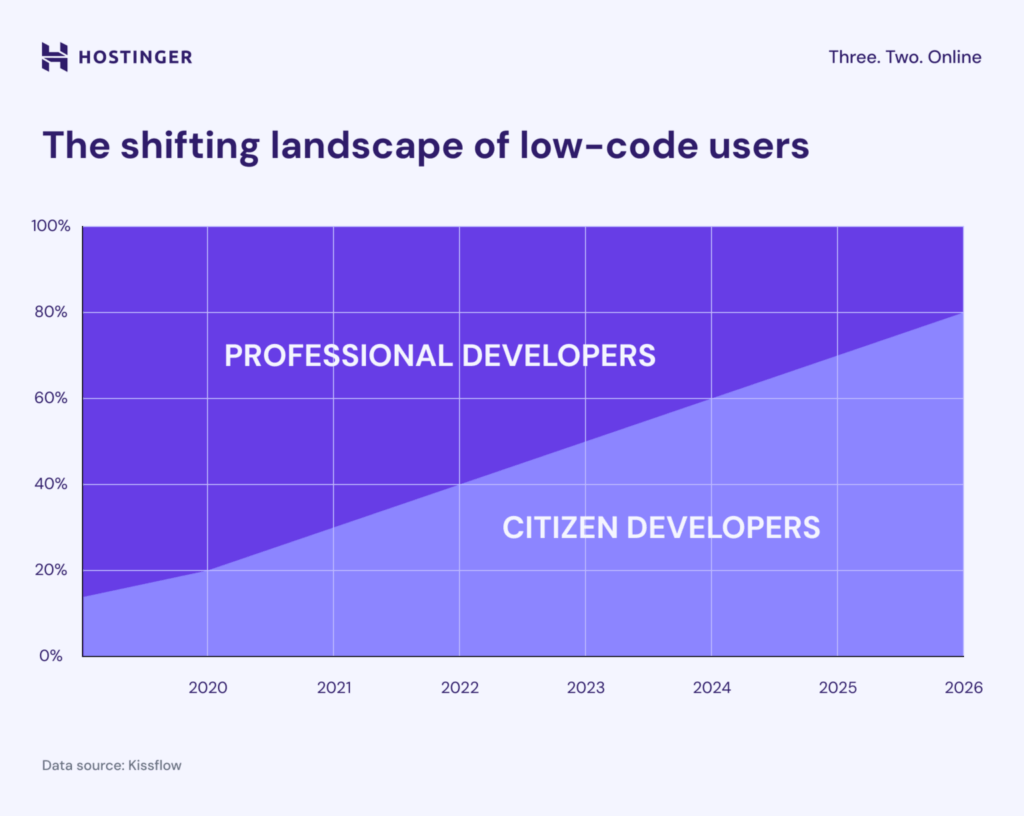
As developer workloads grow and tech talent gets harder to find, more companies and individual business owners are using low-code tools to build their own apps. This has led to a rise in citizen developers: people outside of IT who are expected to become the main users of low-code platforms.
Expert tip
Low-code tools are becoming a practical choice for professionals and businesses looking to build websites quickly and efficiently. They simplify the process by reducing the need for manual coding, making it easier to create and update a site without relying on a developer. Features like AI-generated templates, ecommerce options, and AI support help streamline setup while keeping control in the user’s hands.
Why progressive web apps (PWAs) are becoming more popular
Progressive web apps (PWAs) combine the best of web and mobile applications, delivering fast, reliable, and app-like experiences across devices. As smartphone and mobile internet usage grow, PWAs are becoming more popular for offering seamless functionality without the need for app store downloads.
- $9.4 billion in market size by 2030. The global PWA market is expected to grow from $3.3 billion in 2026, at a CAGR of 31.1%. This growth is driven by increasing smartphone use, internet access, and demand for faster, app-like web experiences. (Grand View Research).
- 6.1 billion smartphone users by 2029. With mobile accounting for 62.5% of global web traffic, the rising use of smartphones is driving the popularity of progressive web apps as a fast, accessible alternative to native apps (Statista).
- PWA market growth led by U.S., Europe, and Asia Pacific. The U.S. market is driven by major tech players and widespread social media use, while Europe’s growth benefits from accelerating digitalization and government initiatives. In the Asia-Pacific region, rising smartphone use, better tech infrastructure, and booming ecommerce are fueling the fastest global rate of market growth (Grand View Research).
- PWAs offer native-like features with standard web technologies. They’re secure, installable, work offline, and adapt to any device. Tasks like file handling, storage, and hardware access can now be done directly on the web instead of needing device-specific code (Microsoft).
Expert tip
Progressive web apps are gaining traction because they offer a native app-like experience through the browser. They support offline access, push notifications, and can be installed without going through an app store. Businesses and creators often choose PWAs for ecommerce storefronts, service sites, dashboards, and interactive content ‒ where speed, reliability, and smooth mobile performance can directly improve engagement and conversion.
How remote and hybrid work is driving cloud computing growth
Remote and hybrid work are driving the move to cloud computing, providing developers with secure and flexible tools to work from anywhere. Cloud-native platforms are now standard for digital workloads, with multicloud and edge computing becoming common.
- $2.29 trillion in market size by 2032. The global cloud computing market continues to rise at a CAGR of 16.6%, growing from $781.27 billion in 2025 to $911 billion in 2026. North America leads with a 52.27% share in 2024 (Fortune Business Insights).
- 95% of new digital workloads are running on cloud-native platforms. With over 85% of organizations adopting a cloud-first approach, cloud-native environments are becoming the norm, while non-cloud setups are increasingly viewed as outdated. (Gartner).
- 92% of companies use a multicloud strategy. Most rely on both public and private cloud platforms, with 96% using at least one public cloud and 84% operating on at least one private cloud (Spacelift).
- 9 in 10 companies report better security after moving to the cloud. Cloud migration also helps almost all businesses meet government compliance requirements more easily (Spacelift).
AI and Zero Trust: Security by design in software development
Zero Trust is a security model that treats all users and devices as untrusted until verified, even within the network. As AI becomes a bigger part of software development, security needs to be built in from the start, not added later. This “secure-by-design” approach helps organizations prevent risks early and protect every step of the development process.
The trends below reflect the growing adoption of Zero Trust in modern software development.
- 96% of security professionals say Zero Trust is critical to success. It’s top of mind for over half of all organizations, especially in the U.S. (56%) and Germany (53%) (Microsoft Security).
- 76% of organizations have started implementing Zero Trust, but only 35% have fully rolled it out. However, among those fully implemented, many still have gaps across key security areas, showing Zero Trust is a work in progress (Microsoft Security).
- 81% of businesses are shifting to a hybrid workplace. While this shift is driving broader adoption of the Zero Trust strategy, 94% express concerns about the transition, mainly around employee misuse, rising IT workloads, and cybersecurity risks (Microsoft Security).
- AI tools are now essential for securing the CI/CD pipeline. They automate code scanning, policy enforcement, and software checks while helping companies meet stricter data security regulations (CybeProof).
- Securing the full AI lifecycle is now a priority. Leaders like CISA and IBM stress protection across data handling, model training, and live use. This aligns with the Shared Responsibility model, which outlines the security tasks handled by the cloud provider and those managed by the customer in cloud AI platforms (IBM).
- 58% of developers feel responsible for application security. This marks a shift from 2023, with more developers now seeing security as part of their role, not just the responsibility of the security team (GitLab).
The future of cybersecurity lies in autonomous defense systems. Powered by machine learning, these tools detect threats by analyzing behavior, going beyond signature-based detection. However, early adopters still face challenges like false alarms and scalability issues (Cloud Security Alliance).
From coding to security: How the developer role is evolving
Introducing AI and the DevSecOps approach, which integrates security at every stage of development, into the continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipeline is reshaping the developer’s role. Beyond writing code, developers now contribute to security, automation, and tool management.
The following trends highlight this evolution and how teams are adapting to these changes.
- $24.43 billion in market value by 2029. The DevSecOps market is set to grow at a CAGR of 28.1%. This growth is driven by rising security needs, increased use of AI and Internet of Things (IoT), and demand for secure, continuous software delivery (The Business Research Company).
- 97 million new roles will emerge as automation grows. While 85 million jobs might be displaced, automation trends point to rising demand for roles focused on managing and operating automated systems (Hostinger).
- 3 in 4 DevSecOps professionals use or plan to use AI in development. At the same time, fewer teams report having no plans to adopt AI, reinforcing that AI in software development is becoming a must-have (GitLab).
- Three-quarters of AI-adopting developers spend just 21% of their time writing new code. The rest is split across tasks like meetings, testing, maintaining and improving code, and managing security, highlighting the need for more efficient workflows (GitLab).
- 74% of AI-adopting DevSecOps teams want to consolidate their toolchain. As developers take on more responsibilities, scattered tools can limit AI’s effectiveness. Simplifying toolchains helps streamline workflows and supports smarter, faster decision-making (GitLab).
- 44% of developers using AI or DevSecOps platforms onboard in under a month. These tools help teams deliver software faster, reduce training time, and boost productivity from day one (GitLab).
What’s next for software development? Future outlook and emerging technologies
The software development industry is evolving quickly, driven by AI, low-code platforms, cloud computing, and security-first approaches like Zero Trust and DevSecOps. These trends are reshaping how teams build, secure, and deliver applications, making development faster, more collaborative, and increasingly automated.
As companies embrace remote work, automation, and better user experiences, developers are taking on broader roles that go beyond writing code. At the same time, low-code tools are opening the door for more non-IT professionals to build applications, signaling a shift in how software is created and who creates it.
Mirroring web development trends, software development is becoming more integrated, secure, and accessible. With AI embedded throughout the software lifecycle and technologies like agentic AI and PWAs gaining momentum, the future of software looks smarter, faster, and more inclusive.
All of the tutorial content on this website is subject to
Hostinger’s rigorous editorial standards and values.